What we'll learn today
- How to access Data Methods
- What are available pages where Data methods can be used
- What are the resources available for the app to consume via data methods.
What we'll need
- A Freshdesk trial account on Modern web browser
- Freshworks CLI
- A code editor
- Basic knowledge of HTML, CSS, Javascript, CLI and Browser DevTools
- The Sample Code (See Get Set Up)
What we'll build
You will explore this feature by writing some simple code to capture a few events like user clicks in app placeholders and explore writing code yourself
Prerequisite Knowledge
- How users use Freshdesk.
- Available placeholders for apps.
- Have walked through code of an Freshworks App
- Awareness of App Lifecycle Methods
Get the sample code ready
git clone https://github.com/freshworks-developers/data-methods-freshdesk.git
Alternatively,
[Download the Zip] (https://github.com/freshworks-developers/data-methods-freshdesk/archive/main.zip)
Verify
- Open the cloned repository in the code editor with ‘start' branch.
- Open Terminal and run
> fdk run - You should notice the app is being served at
localhost:10001 - Login to Freshdesk trial account and pay attention to four placeholders after appending
?dev=trueat every page. You should see an app icon available to activate the app.
Note: The Data Methods can be invoked specific to the placeholders. See documentation for specific details.
Data Methods allow your app to access information on a given Freshdesk page. In this tutorial you'll learn how to consume data methods in your freshworks apps.
client.data.get(" returns a promise where your callback would have access to data in the page which user is currently viewing.
Let's see this in action.
❯ fdk run
Starting local testing server at http://*:10001/
Append 'dev=true' to your Freshdesk account URL to start testing
e.g. https://domain.freshdesk.com/a/tickets/1?dev=true
Quit the server with Control-C.
Freshworks CLI serves your app to the browser on port :10001. In the Freshdesk account, append the URL with ?dev=true to find apps running on the global sidebar at CTI app location.
Data Methods return the data that the app needs based on the app placeholders. Mostly giving the contextual information pertaining to the current page. However, the following arguments can be passed to the Data method that would return the payload given in any placeholder.
loggedInUser
The following is how you can consume it in your app
client.data
.get('loggedInUser')
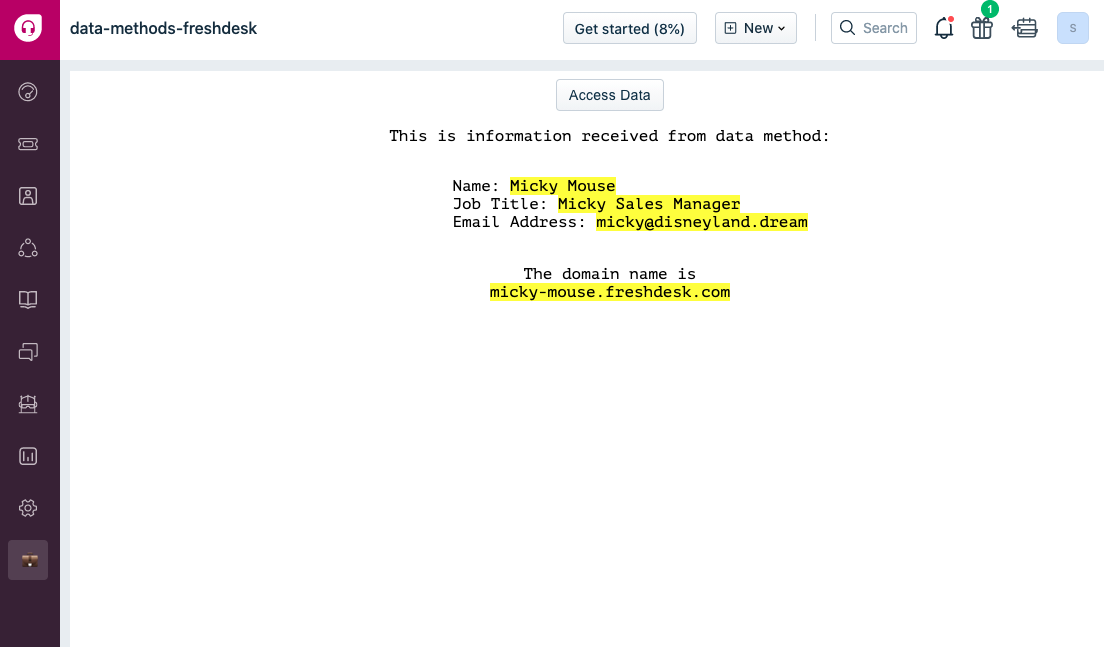
.then(function renderUserBioData(payload) {
var {
loggedInUser: {
contact: { name: name, job_title: job, email: email }
}
} = payload;
displayArea.insertAdjacentHTML(
'afterbegin',
`<p>This is information received from data method:</p>
<ul>
<li>Name: <mark>${name}</mark></li>
<li>Job Title: <mark> ${job} </mark></li>
<li>Email Address: <mark> ${email} </mark></li>
</ul>
`
);
})
.catch(console.error);
Let's discuss this in detail.
clientis an object that is brought into scope for the developer by the platform. See Line 6 in app/scripts/fullpage.js is attaching it to the global scope of the window.client.data.get()is a method that can interface with Freshdesk (via platform) and get the information for the app to consume.- In the above code snippet, an argument of type string
loggedInUseris passed to theget()method. It returns a promisealong with a payload. In this case, a payload containing the information ofloggedInUser. - This payload becomes available within the scope of the callback function that is passed. Here, the callback is
renderUserBioData(payload){..} The renderUserBioData(payload){..}function does two things. It is assigning the payload data toname,jobandemailvariables. Also, rendering the samename,jobandemailinformation to the DOM. [See object destructuring if you find the assignment confusing.]- That's how the payload passed can be consumed by the app.
Note: Always refer to the documentation for latest payload structure and attribute definitions.
domainName
client.data
.get('domainName')
.then(function whatsDomain({ domainName }) {
displayArea.insertAdjacentHTML('afterend', `<br> The domain name is <mark>${domainName}</mark>`);
})
.catch(console.error);
This snippet simply fetches the host Freshdesk's domain name for the app.
See the current state of source code on global-args branch of sample code.
Each page has a couple of placeholders for the app. Just like Global Arguments can be passed to the data method in any page or app placeholder. However, data is provisioned (via data methods) to the app based on the page app is placed in.
For this tutorial, let's look at Ticket details page,
Ticket Details Page
Open app/scripts/sidebar.js and try adding some methods consuming different valid arguments ticket details page.
Within the renderSidebar(){..},
// ticket
client.data
.get('ticket')
.then(function getDetails({ ticket: { description_text: desc, priority: priority } }) {
space.insertAdjacentHTML(
'afterbegin',
`<li><i>"ticket"</i> priority: <mark>${priority}</mark> : desc: <mark>${desc}</mark></li>`
);
})
.catch(console.error);
//contact
client.data
.get('contact')
.then(function getDetails({ contact: { address: address, name: name } }) {
space.insertAdjacentHTML(
'afterbegin',
`<li><i>"contact"</i> address: <mark>${address}</mark> name: <mark>${name}</mark></li>`
);
})
.catch(console.error);
// email_config
client.data
.get('email_config')
.then(function getDetails(payload) {
let supportEmail = payload.email_config[0].replyEmail;
space.insertAdjacentHTML('afterbegin', `<li><i>"email_config"</i> : <mark>${supportEmail}<mark></li>`);
})
.catch(console.error);
//requester
client.data
.get('requester')
.then(function getDetails(payload) {
let name = payload.requester.name;
space.insertAdjacentHTML('afterbegin', `<li><i>"requester"</i> : <mark>${name}<mark></li>`);
})
.catch(console.error);
//requester
client.data
.get('company')
.then(function getDetails(payload) {
let name = payload.company.name;
space.insertAdjacentHTML('afterbegin', `<li><i>"company"</i> : <mark>${name}<mark></li>`);
})
.catch(console.error);
//requester
client.data
.get('group')
.then(function getDetails(payload) {
let name = payload.group.name;
space.insertAdjacentHTML('afterbegin', `<li><i>"group"</i> : <mark>${name}<mark></li>`);
})
.catch(console.error);
//requester
client.data
.get('company')
.then(function getDetails(payload) {
let name = payload.company.name;
space.insertAdjacentHTML('afterbegin', `<li><i>"company"</i> : <mark>${name}<mark></li>`);
})
.catch(console.error);
//status_options
client.data
.get('status_options')
.then(function getDetails(payload) {
let opt = payload.status_options[0];
space.insertAdjacentHTML('afterbegin', `<li><i>"status options"</i> First option: <mark>${opt}<mark></li>`);
})
.catch(console.error);
//time_entry
client.data
.get('time_entry')
.then(function getDetails(payload) {
let isTimerRunning = payload.time_entry.time_entries[0].time_spent;
space.insertAdjacentHTML('afterbegin', `<li><i>"time entry"</i> First option: <mark>${isTimerRunning}<mark></li>`);
})
.catch(console.error);
The result would be information rendered to the DOM informing of a list in the ticket sidebar returned from different data methods.
ticket_sidebar
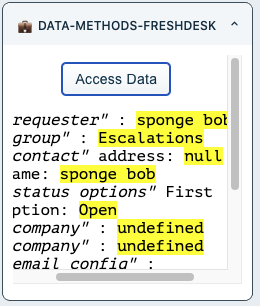
full_page_app
At this point you have consumed data methods from Global Arguments and Ticket Details Page specific arguments.
Bunch of other locations where Data Methods can be accessed are
- Ticket Details Page:
ticket,contact,email_config,requester,company,group,_options time_entry - New Ticket Page:
_options - New Email Page:
email_cofig,_options - Contact Details Page:
contact,company
Why not try writing code yourself for requesterpage.js and contactpage.js ?
- Try to understand the existing code and it's associated html and css files.
- Surf through documentation to see valid arguments at these placeholders.
- Try picking up a few of those payloads and writing to the DOM.
Above steps will give you more confidence using the Data Methods.
Congratulations! 💐
You have come so far walking throughout the tutorial.